|
Eugenio,77
Daihatsu ·
Honda ·
Mazda ·
Mitusbishi ·
Nissan ·
Subaru ·
Suzuki ·
Toyota ·
Hyundai
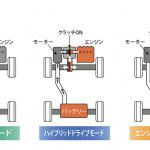
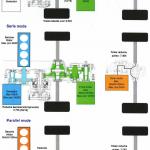
Since the beginning of the 2010s, Daihatsu has been offering Toyota hybrid cars under own brand, and then in 2021 they implemented a series hybrid scheme that is fundamentally new for the entire TMC. • e-SMART ○ Concept: series hybrid. The transmission with a fixed gear ratio contains two electric motors - the generator driven by internal combustion engine and the traction motor. The internal combustion engine is used to drive the generator only. ○ Operation modes:
(1) wheel drive by electric motor, power supply from battery; ○ System total power: Determined by the electric motor power. • HSD (Toyota) ○ Concept: series-parallel hybrid. Rebadged models (Altis ⇐ Camry, Mebius ⇐ Prius) are identical in design and specs to the corresponding models of Toyota.
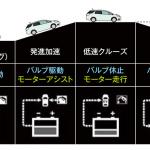
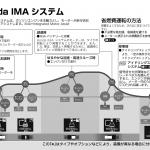
Honda became the second hybrid manufacturer in Japan when introduced Insight in 1999. For a long time, the company used a simple IMA scheme with a low-power electric motors, but at last presented two new full-fledged schemes in 2012: the AMT-based parallel hybrid i-DCD for compact models and the innovative series-parallel i-MMD for the medium-size vehicles. Before the beginning of the 2020s, the i-MMD scheme became part of the global 'e:HEV' concept (later 'e:PHEV' also appeared) and was expanded to compact-class vehicles, gradually replacing i-DCD. • IMA (Integrated Motor Assist) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid (mild hybrid). Auxiliary motor-generator is integrated between the internal combustion engine and conventional transmission. ○ Operation modes:
(1) wheel drive by ICE; ○ System total power: Determined by summing the ICE power and the electric motor power. • i-DCD (intelligent Dual-Clutch Drive) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid. Automated manual transmission (dual-clutch type, 7-speed) with integrated motor-generator. ○ Operation modes:
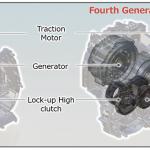
(1) wheel drive by electric motor; ○ System total power: Determined by summing the ICE power and the electric motor power. ○ Особенности: 'Sport Hybrid Super Handling All-Wheel Drive' - i-DCD variation with twin electric motors for rear wheel drive (MDX, RLX, Legend). • i-MMD / e:HEV (intelligent Multi-Mode Drive) ○ Concept: series-parallel hybrid. The transmission with a fixed gear ratio contains two electric motors - the generator driven by internal combustion engine and the traction motor. The [overdrive] clutch allows to use direct mechanical drive from ICE to the wheels. PHEV version allows battery recharge from external power source. The first generations had a coaxial layout of electric motors, for the fourth generation the motors were installed in parallel and the second clutch was added. ○ Operation modes:
(1) wheel drive by motor, power supply from battery; ○ System total power: Determined by partial summing of the ICE power and the electric motor power. Depending on the market and model, Honda specifies the value of total system power, or specifies the maximum power of ICE and electric motors separately, or stipulates that the total (Gesamt) power is determined by the power of traction motor.
Mazda's first hybrid is Tribute HEV '2007 (aka Ford Escape Hybrid) that combined own Ford engine with Toyota's hybrid transmission; this practice was later repeated in Axela '2013. Since 2015, the company has been selling Suzuki hybrid kei-cars under own brand, since 2022 - some Toyota hybrid models. Own MHEV scheme was introduced in the late 2010s for FF-layout cars. And finally, in 2022, a full-fledged PHEV scheme was implemented for cars on a new FR-layout platform. • e-4WD ○ Concept: parallel hybrid. The conventional transmission to drive the front wheels and a separate electric motor to drive the rear ones. Power for the electric motor (3.5 kW) is supplied by enforced generator. Used for Demio DY / Verisa. • M Hybrid (e-Skyactiv) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid (mild hybrid). The conventional engine is complemented by the starter-generator (ISG) with a belt drive (system voltage 24V). ○ Operation modes:
(1) stop-start function, engine restart by motor; • M Hybrid Boost (e-Skyactiv) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid (mild hybrid). The motor-generator (16 kW) is integrated between the internal combustion engine and transmission (system voltage 48V). ○ Operation modes:
(1) stop-start function, engine restart by motor; ○ System total power: Determined by summing the ICE power and the electric motor power. • PHEV (e-Skyactiv) ○ Concept: parallel plug-in-hybrid. The motor-generator (130 kW) is integrated between the internal combustion engine and transmission (high-voltage system). ○ Operation modes:
(1) wheel drive by electric motor; ○ System total power: Determined by summing the ICE power and the electric motor power. • HSD (Toyota) ○ Concept: series-parallel hybrid. The rebadged models (Famila Van ⇐ Probox, Mazda2 ⇐ Hybrid Yaris) are identical in design and specs to the corresponding Toyota models. Axela Hybrid uses a Toyota HSD hybrid powertrain similar to Prius ZVW30, but paired with Mazda engine.
The only original, but progressive product of the company was the PHEV scheme, introduced in 2013. The remaining hybrid cars under Mitsubishi brand are rebadged models of Suzuki, Nissan, Renault. • MHEV (Suzuki) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid (mild hybrid). Starter-generator with a belt drive. Used for rebadged Suzuki models (Delica D:2 ⇐ Solio) • MHEV (Renault) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid (micro-hybrid). Starter-generator with a belt drive (system voltage 12V). Used for rebadged Renault models (ASX ⇐ Captur) • MHEV (Nissan) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid (mild hybrid). Starter-generator with a belt drive, auxiliary battery. Analog of the Nissan S-Hybrid for co-developed kei-cars. • IDCC (Nissan) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid. Automatic transmission with integrated motor-generator. Used for rebadged Nissan FR-layout models (Dignity ⇐ Fuga). • e-TECH (Renault) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid. The transmission is a three-shaft manual gearbox without synchronizers and clutches, combined with a traction motor-generator and an auxiliary starter-generator. Used for rebadged Renault models (ASX ⇐ Captur) ○ Operation modes:
(1) wheel drive by electric motor; ○ System total power: Determined by summing the ICE power and the electric motor power. • e-TECH PHEV (Renault) ○ Concept: parallel plug-in-hybrid. e-TECH scheme with high capacity battery and external recharging capability. Used for rebadged Renault models (ASX ⇐ Captur) • PHEV (Mitsubishi) ○ Concept: series-parallel plug-in-hybrid. The transmission with a fixed gear ratio contains two electric motors - the generator driven by internal combustion engine and the traction motor. The multiplate clutch allows to use direct mechanical drive from ICE to the front wheels. Separate electric motor drives the rear wheels. ○ Operation modes:
(1) wheel drive by motors, power supply from battery; ○ System total power: Determined by partial summing of the ICE power and the electric motors power.
The first hybrid Nissan appeared in 2007 - Altima was equipped with own engine and Toyota's transmission. In 2010, the first original IDCC scheme for FR-layout models appeared; since 2012, mild hybrids have been produced under the 'S-Hybrid' name; in 2015, the IDCC scheme was implemented for FF-layout models with CVT. But Nissan's main achievement in this area was introduction of e-Power pure series hybrid scheme. In addition, Renault hybrid transmission can be used for European market models. • e-4WD ○ Concept: parallel hybrid. The conventional transmission to drive the front wheels and a separate electric motor to drive the rear ones. Power for the electric motor (3.5 kW) is supplied by enforced generator. Used for March, Cube, Tiida, Note, Bluebird Sylphy, Wingroad, created in the 2000s. • S-Hybrid (Smart Simple Hybrid) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid (mild hybrid). The conventional engine is equipped with the belt drive starter-generator (Eco-motor) and auxiliary battery is attached. ○ Operation modes:
(1) stop-start function, engine restart by motor; • IDCC (FR) (Intelligent Dual Clutch Control) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid. The automatic transmission with integrated motor-generator is connected to ICE and to propeller shaft via clutches. Used for FR-layout models. ○ Operation modes:
(1) wheel drive by electric motor, power supply from battery; ○ System total power: Determined by summing the ICE power and the electric motor power. • IDCC (FF) (Intelligent Dual Clutch Control) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid. The motor-generator is integrated in transmission, connects to ICE and CVT via clutches. Used for FF-layout models. ○ Operation modes:
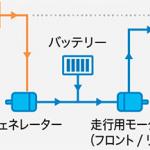
(1) wheel drive by electric motor, power supply from battery; ○ System total power: Determined by summing the ICE power and the electric motor power. • e-Power ○ Concept: series hybrid. The transmission with a fixed gear ratio contains two electric motors - the generator driven by internal combustion engine and the traction motor-generator. Separate electric motor drives the rear wheels (4WD models). The internal combustion engine is used to drive the generator only. ○ Operation modes:
(1) wheel drive by motor, power supply from battery; ○ System total power: Determined by the electric motor power. Depending on model and market, the power of rear electric motor can be partially taken into account. • MHEV (Renault) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid (micro-hybrid). The conventional engine is equipped with the belt drive starter-generator (ISG), system voltage 12V. • e-TECH (Renault) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid. The transmission is a three-shaft manual gearbox without synchronizers and clutches, combined with a traction motor-generator and an auxiliary starter-generator. ○ Operation modes:
(1) wheel drive by electric motor; ○ System total power: Determined by summing the ICE power and the electric motor power.
Since 2013, the company has been promoting e-Boxer scheme, which despite a rather complicated design, is just about MHEV level in terms of abilities; since 2018, the only full-fledged hybrid based on Toyota components has been produced. • StarDrive ○ Concept: series-parallel hybrid. The electric continuously variable transmission includes two motor-generators MG1 and MG2 and a planetary power distribution device which is simultaneously connected to the internal combustion engine, MG1 and the wheels. Rear wheel drive - mechanical. The system is based on Toyota HSD components (version with 3NM electric motor). ○ Operation modes:
(1) wheel drive by electric motor; ○ System total power: Determined by partial summing of the ICE power and the traction motor-generator power. • e-Boxer ○ Concept: parallel hybrid. The V-chain type continuously variable transmission with integrated motor-generator is connected to the wheels via additional clutch. ○ Operation modes:
(1) wheel drive by electric motor; ○ System total power: Determined by the power of the internal combustion engine. Depending on model and market, the total value can be determined by summing the powers of ICE and motor (118kW/160PS).
Suzuki's early designs did not go beyond the concept stage, so mass hybridization (simplest MHEV scheme) began in 2014 with kei-cars, and soon starter-generators appeared on most of the company's models. The first full-fledged hybrid based on automated manual transmission with attached electric motor appeared only in 2022. A parallel direction is cooperation with Toyota - in the format of rebadging entire vehicles or installing Toyota powertrains in their own models. • SHVS / ISG (Smart Hybrid Vehicle by Suzuki) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid (mild hybrid). The conventional engine is equipped with the belt drive starter-generator (ISG), the auxiliary battery is attached (system can be implemented in 12V or 48V versions). ○ Operation modes:
(1) stop-start function, engine restart by ISG; • Hybrid / MGU (Full Hybrid / Strong Hybrid) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid. Automated manual transmission with integrated motor-generator, 140V battery is attached. Engine can be equipped with ISG. ○ Operation modes:
(1) stop-start function, engine restart by motor; ○ System total power: Determined by summing the ICE power and the electric motor power. • HSD (Toyota) ○ Concept: series-parallel hybrid. The rebadged models (Across ⇐ RAV4 PHEV, Swace ⇐ Corolla Touring Sport, Landy ⇐ Noah) and co-developed models (Grand Vitara - Urban Cruiser Hycross) are identical in design and specs to the corresponding Toyota models. • S-Hybrid (Nissan) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid (mild hybrid). Belt drive starter-generator. Used for rebadged Nissan models (Landy ⇐ Serena).
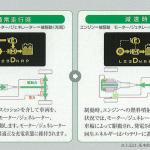
Prius '1997 was the first mass-production passenger car for both Toyota and the world. From the very beginning, the company has preferred a series-parallel hybrid scheme with a planetary power distribution device (THS / THSII / HSD), retaining this concept with all non-core design modifications, although several experiments with alternative schemes were undertaken in the 2000s. The parallel hybrid system used for a new generation of full-size SUVs can be seen just as evolution of ideas long known from Hino trucks. And the first fundamental innovation became the DBHS parallel hybrid scheme in 2022. • THS-M (Toyota Hybrid System - Mild) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid (mild hybrid). The conventional engine is equipped with the belt drive starter-generator, the auxiliary battery is attached (system voltage 36V). ○ Operation modes:
(1) stop-start function, engine restart by electric motor; • THS-C (Toyota Hybrid System - CVT) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid. V-belt type continuously variable transmission with integrated motor-generator and power distribution clutch. Separate electric motor drives the rear wheels. ○ Operation modes:
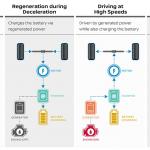
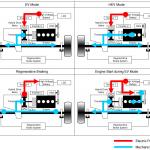
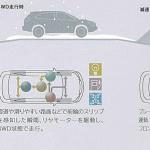
(1) wheel drive by electric motors; ○ System total power: Determined by summing the powers of internal combustion engine and front electric motor (the value is not standardized by the manufacturer). • THSII / HSD (Toyota Hybrid System / Hybrid Synergy Drive) ○ Concept: series-parallel hybrid. The electric continuously variable transmission contains two motor-generators MG1 and MG2 and a planetary power distribution device which is simultaneously connected to the internal combustion engine, MG1 and the wheels. The rear wheels are driven by separate MGR motor-generator (e4WD versions). ○ Operation modes (2WD):
(1) wheel drive by electric motor, battery powered; ○ Operation modes (e4WD):
(1) front wheel drive by motor, rear wheel drive by motor (if necessary), power supply from battery; ○ System total power: Determined by partial summing of the ICE power and the traction motor-generator power. • HSD (FR) (Hybrid Synergy Drive) ○ Concept: series-parallel hybrid. There are three powertrain options for FR-layout models - simplified (following HSD principles), with 2-speed or with 4-speed gearboxes. ○ Operation modes:
(1) wheel drive by motor, power supply from battery; ○ System total power: Determined by partial summing of the ICE power and the traction motor-generator power. • HSD PHEV ○ Concept: series-parallel plug-in-hybrid. The first version differs from conventional HSD by a high-capacity battery and external charging capability. The second version, in addition, allows the motor-generator MG1 to operate as a traction motor together with MG2 while driving in EV mode. ○ System total power: Determined by partial summing of the ICE power and the traction motor-generator power. Rear electric motor power is partially taken into account. • DBHS / T-HEV (Dual Boost Hybrid System / Turbo-HEV) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid. The motor-generator is integrated in 6-speed automatic transmission and connects to ICE via the multiplate clutch. The rear wheels are driven by a separate electric motor (eAxle). ○ Operation modes:
(1) wheel drive by motors, power supply from battery; ○ System total power: Determined by summing the ICE power and the electric motor power. • HEV (Truck) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid. The motor-generator is integrated between the conventional internal combustion engine and transmission, connects to ICE via the clutch. Used for full-size FR-layout SUVs. ○ Operation modes:
(1) wheel drive by electric motor; ○ System total power: Determined by summing the ICE power and the electric motor power. • e-SMART (Daihatsu) ○ Concept: series hybrid. Rebadged models (Raize ⇐ Rocky) are identical in design and specs to the corresponding models of Daihatsu.
HMC hybrid history dates back to the 2011 model year and Hyundai Sonata/Kia Optima pair, and the scheme chosen at that time continues its development in the regular and plug-in versions. Modifications that have not received a full-fledged hybrid powertrain are mostly equipped as MHEV. • MHEV ○ Concept: parallel hybrid (mild hybrid). The conventional engine is equipped with the belt drive starter-generator (MHSG), the auxiliary battery is attached (system voltage 48V). • HEV ○ Concept: parallel hybrid. The motor-generator is built-in between the engine and transmission, connects to ICE via [engine clutch]; the engine is also equipped with the starter-generator. ○ Operation modes:
(1) wheel drive by electric motor; ○ System total power: Determined by summing the ICE power and the electric motor power. • PHEV ○ Concept: parallel plug-in-hybrid. It differs from conventional hybrid version with a more powerful electric motor, large-capacity battery and the possibility of recharging from an external source.
The first hybrid model of Korean Renault is rebadged Arkana with a French transmission. • e-TECH (Renault) ○ Concept: parallel hybrid. The transmission is a three-shaft manual gearbox without synchronizers and clutches, combined with a traction motor-generator and an auxiliary starter-generator. Used for rebadged Renault models (ASX ⇐ Captur) ○ Operation modes:
(1) wheel drive by electric motor; ○ System total power: Determined by summing the ICE power and the electric motor power.
App.2. Reference values for 30-minute power of electric motors (European market models):
HEV typology :
Toyota HSD ·
Daihatsu e-Smart ·
Honda i-MMD (e:HEV) ·
Toyota Hybrid:
E-Four ·
THS-C ·
HEV trans ·
BEV/FCEV ·
HEV trucks
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||